Largest Selection of New and Used Office Furniture! Call 1-855-885-3375 or visit a showroom today!
Blog
How to Use Tibial Interlocking Nail for Bone Fractures?
In the realm of orthopedic surgery, the Tibial Interlocking Nail has become a critical tool for managing severe bone fractures. Dr. Jane Smith, a leading expert in orthopedic procedures, states, “The Tibial Interlocking Nail not only stabilizes the bone but also encourages healing.” This innovative device allows for precise alignment and fixation of fractured tibia, helping patients regain mobility.
Patients often face challenges in recovery from such injuries. The Tibial Interlocking Nail is designed to address these issues effectively. Its interlocking features enhance stability, yet the insertion technique requires careful consideration. Surgeons must navigate various elements, such as patient anatomy and fracture type, to achieve optimal results. The process is complex, and mistakes can occur, underscoring the need for meticulous training and practice.
While the benefits are substantial, it’s essential to acknowledge potential complications. Though rare, issues can arise post-surgery. An example might include infection or improper alignment. Recognizing these challenges is crucial for successful implementation of the Tibial Interlocking Nail. The journey toward healing is often multifaceted and requires continuous reflection and adaptation from medical professionals.
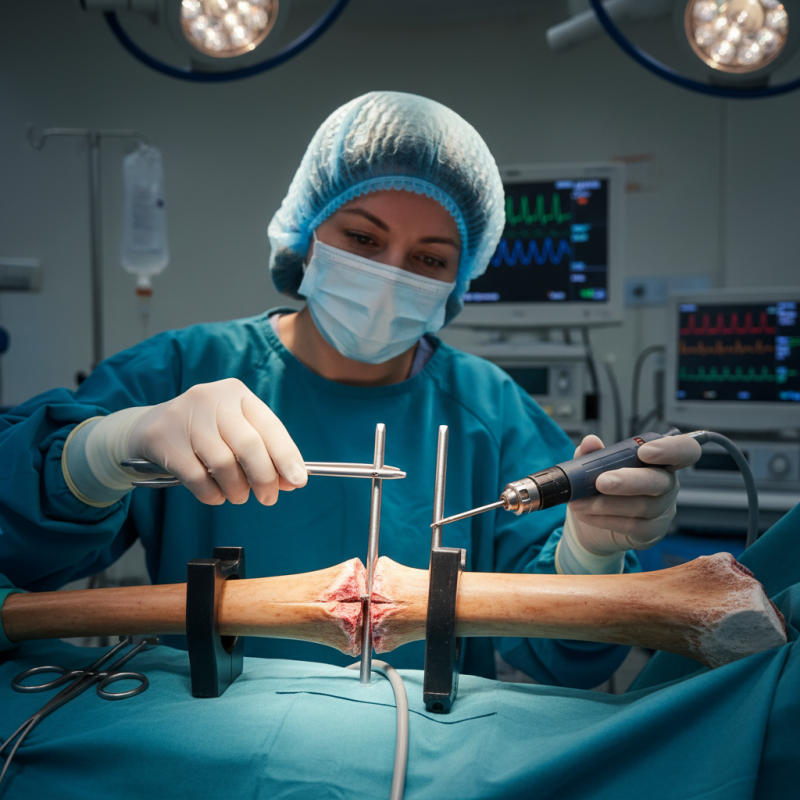
Overview of Tibial Interlocking Nail and Its Indications
Tibial interlocking nails are crucial in treating bone fractures. They provide stable fixation, allowing for early mobilization. According to a study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery, the successful union rate for tibial fractures treated with interlocking nails is around 95%. This high success rate highlights the method’s effectiveness in improving patient outcomes.
Indications for using tibial interlocking nails include fractures of the tibial shaft, particularly in cases of unstable or displaced fractures. These nails can be inserted through a minimally invasive approach, which is advantageous for soft tissue preservation. Tips for surgeons include ensuring proper alignment of the nail to avoid malunion. This can significantly affect healing and patient recovery times.
Close monitoring of the patient’s progress is essential. Any signs of infection or nonunion should be addressed promptly. Patients should be educated about their recovery process. Regular follow-ups ensure any complications are managed early. Remember, while interlocking nails are effective, they are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each case should be evaluated individually to determine the best fixation method.
Tibial Interlocking Nail Application in Bone Fractures
Preoperative Planning and Patient Assessment for Fracture Treatment
Preoperative planning is crucial in the treatment of tibial fractures using interlocking nails. A comprehensive patient assessment helps in determining the best surgical approach. Factors such as age, bone quality, and fracture pattern play essential roles. According to a study by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, more than 70% of patients with tibial fractures are younger than 50. This demographic often exhibits better healing potential, yet individual patient factors must be considered.
During the assessment, clear imaging is vital. X-rays and CT scans provide crucial information about fracture alignment. This helps in determining the appropriate nail length and diameter. A miscalculation here can lead to complications. A report from the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma highlights that malalignment can occur in about 20% of tibial nail procedures. Surgeons must educate patients on these risks during preoperative discussions, ensuring that they understand what to expect. Furthermore, assessing comorbidities like diabetes or smoking habits can influence recovery timelines.
Surgeons should consider all angles. Are there soft tissue injuries? How about the patient’s lifestyle? Emotional readiness also matters. Prematurely optimistic expectations can lead to dissatisfaction post-surgery. Research shows that outcomes can vary widely based on patient adherence to rehabilitation protocols. Engaging patients in their care plan can boost both compliance and overall outcomes.
How to Use Tibial Interlocking Nail for Bone Fractures? - Preoperative Planning and Patient Assessment for Fracture Treatment
| Assessment Criteria | Description | Importance | Preoperative Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient History | Medical history including previous fractures and surgeries. | Helps identify risk factors for complications. | Review total health and any contraindications. |
| Imaging Studies | X-rays or CT scans to determine fracture type and location. | Guides surgical approach and nail selection. | Ensure correct imaging protocol is followed. |
| Physical Examination | Assess swelling, deformity, and neurovascular status. | Evaluates the fracture’s impact on function. | Perform a thorough assessment of the limb. |
| Blood Tests | Complete blood count and metabolic panel. | Identifies potential anesthetic risks and healing prognosis. | Prepare for safe anesthesia and surgery. |
| Anesthesia Assessment | Evaluation for general or regional anesthesia. | Ensures patient safety and comfort during surgery. | Discuss potential complications with the anesthesia team. |
Surgical Technique for Inserting Tibial Interlocking Nail
Inserting a tibial interlocking nail is a significant technique for treating bone fractures. The procedure begins with preparing the patient. Anesthesia is administered, and the limb is carefully positioned. The surgeon makes an incision over the fracture site. This allows for direct access to the tibia. A careful examination of the fracture is essential. This ensures the nail will align correctly during insertion.
Next, a reamer is utilized to create a pathway in the bone. This step is crucial; any mistake can lead to complications. The interlocking nail is then inserted through the hole created. The alignment must be perfect, allowing the nail to stabilize the fracture efficiently. After insertion, locking screws are placed. These are vital for maintaining the position of the nail. It can be challenging to achieve optimal lock placement on the first try.
Throughout the procedure, careful monitoring is necessary. The surgeon must check for signs of infection or improper alignment. Post-operative care is equally important. Patients often require physiotherapy to regain strength. Reflecting on the procedure reveals areas for personal improvement, especially in precision and technique. Each surgery offers learning opportunities for growth. The journey in mastering this surgical skill is ongoing and requires practice and patience.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation Following Nail Insertion
Postoperative care is crucial after tibial interlocking nail insertion. It sets the stage for successful recovery. Pain management is often a top priority. Your doctor may prescribe medications to help reduce discomfort. It's essential to follow the dosing instructions carefully. Pain can hinder your ability to engage in rehabilitation exercises.
Movement is vital in this phase. Gentle, guided exercises help maintain mobility. However, pushing through pain can lead to setbacks. Listen to your body, and do not rush. Activities like ankle pumps can be beneficial without putting stress on the healing site.
Tips: Keep your incision clean and dry. Regularly monitor for signs of infection, such as redness or swelling. Staying hydrated aids recovery, but be cautious with fluid intake if you're limited in mobility. After the first few weeks, gradually increase your activity level. Communicate any unusual sensations to your healthcare provider.
Potential Complications and Management Strategies in Bone Healing
The use of a tibial interlocking nail can significantly aid in the healing of bone fractures. However, several potential complications may arise during this process. Patients often face issues such as infection, malunion, or delayed healing. These complications can lead to prolonged recovery periods and require careful management. Surgeons must monitor the site closely, looking for signs of inflammation or abnormal pain.
Infection is a primary concern following surgery. It can develop due to dirty environments or improper care of the wound. Management strategies include keeping the operation site clean and using antibiotics as necessary. Malunion occurs when the bone does not heal in the correct position. This may necessitate additional procedures. Surgeons should educate patients about the importance of following postoperative instructions.
Delayed healing presents another complication. Factors such as age, nutrition, and smoking can affect recovery. Encourage patients to maintain a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D. Regular follow-ups are crucial in identifying and addressing complications early. Reflection on these potential issues can lead to better outcomes in patient care.
